Huckel's Rule 4n2 = Number of Resonating Electrons Resonating electrons include both pi electrons and lone pairs When solving for 'n', n must equal to a whole number If we get a fraction then the molecule DOES NOT obey Huckel's rule Benzene is the most common aromatic molecule a benzene ring has 3 pi bonds thus 6 resonatingAromatic (ring) compounds must have 4 n 2 pibonding electrons, where n is a whole number and generally limited to n = 0 to 5 When n = 1, for example, there are six pielectrons, as for benzene Also known as Hückel's ruleAromaticity can be predicted by the use of Huckle's rule which says that (4n 2) $\pi$electrons are required in delocalisation system to give it aromaticity (4n 2) $\pi$ electrons means 2, 6, 10 $\pi$ electrons

Applying The Criteria For Aromaticity Mcc Organic Chemistry
4n + 2 pi electrons aromatic
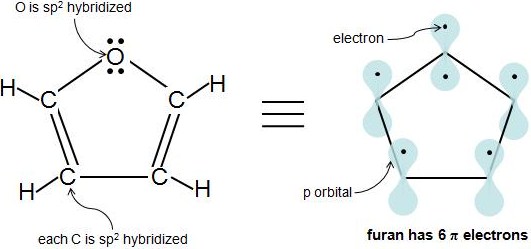
4n + 2 pi electrons aromatic-So while aromatic molecules have (4n2) pi electrons, the "rule" for anti aromatic molecules is (4n) (This unusual instability is called "antiaromaticity" This means that we can now draw up three categories for molecules according to the following criteria Aromatic molecules are cyclic, conjugated, have (4n2) pi electrons, and areIf n=1, 4n2 = 6 > 6 pi electrons in a ring is aromatic > benzene is an example if the number of pi electrons does NOT equal 4n2 for any value of n, the ring is not aromatic > example here is butadiene furan 2 double bonds in the ring, and 1 lone pair on the O participate in pi bonding total of 6 pi electrons, ring is aromatic
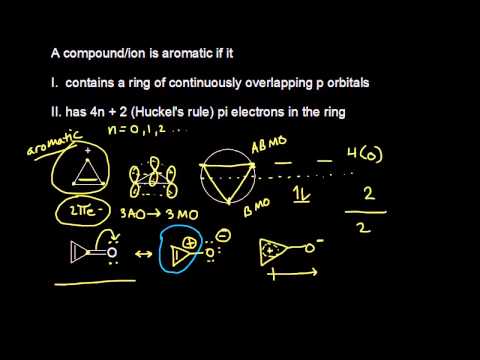


Aromatic Stability Iii Video Khan Academy
4n2 pi electrons always means aromatic All this formula means is that it has odd pairs of pi electrons Anti aromatic Compounds 4n pi electrons cyclic, conjugated polyenes that are destabilized because they have electrons in higher energy nonbonding or antibonding orbitals (Even pairs of pi electrons) PhCOOH Benzoic acidN is just any natural number which is used to satisfy the 4n 2 rule 1 Count the number of pi electrons 2 If that number becomes equal 4n 2 for any value of n then that compound is aromatic(or in other words if the number of pi electrons come in the series – 2, 6, 10, 14, 18 then that compound will be aromatic)Huckel's Rule 4n2 = Number of Resonating Electrons Resonating electrons include both pi electrons and lone pairs When solving for 'n', n must equal to a whole number If we get a fraction then the molecule DOES NOT obey Huckel's rule Benzene is the most common aromatic molecule a benzene ring has 3 pi bonds thus 6 resonating
However, if the carbocation moiety is contained in a cyclic, conjugated system having 4n2 pi electrons, the carbocation may be stable enough even to isolate as a salt q A particularly impressive example of an aromatic carbocation is the cycloheptarienyl (tropylium) carbocation, This cation, like benzene and the cyclopentadienyl anion, has aThe Huckel 4n 2 Pi Electron Rule A ringshaped cyclic molecule is said to follow the Huckel rule when the total number of pi electrons belonging to the molecule can be equated to the formula '4n 2' where n can be any integer with a positive value (including zero)Furan In furan, there are two lone pairs on oxygen and hence, it
Hückel's Rule dictates a flat ring with 4n 2 π (pi) conjugated electrons The smallest neutral ring with these qualifications has n = 1 It is benzene (C₆H₆) But Hückel's law does not require an electronically neutral structureThe pi electron count is defined by the series of numbers generated from 4n2 where n = zero or any positive integer (ie, n = 0, 1, 2, etc) The most common case in six pi electrons (n = 1) which is found for example in benzene, pyrrole, furan, and pyridineBut, antiaromatic compounds have a closed loop of 4n pibond electrons Below are the piorbital diagrams of benzene, the most identifiable aromatic compound Each of the three double bonds contributes 2 pielectrons over 6 atoms, for a total of 4*12=6 electrons, in a ring, in a piorbital that is planar Therefore it is aromatic



Simple Trick To Find Aromatic Compounds Huckel S Rule 4n 2 Pi Electrons Rule Youtube



Criteria For Aromaticity 1 The System Must Be Cyclic 2 The System Must Be Planar Flat 3 Each Ring Atom Must Be Part Of A Completely Extended Pi System Ppt Download
The one in the middle has a 4n number of pi electrons (where n=1), so it's antiaromatic The carbanion can resonate with the double bond, which means the molecule is fully conjugated This is an antiaromatic ion The one on the right is fully conjugated and has a 4n2 number of pi electrons (where n=0), so it's aromatic The carbocation hasThe one in the middle has a 4n number of pi electrons (where n=1), so it's antiaromatic The carbanion can resonate with the double bond, which means the molecule is fully conjugated This is an antiaromatic ion The one on the right is fully conjugated and has a 4n2 number of pi electrons (where n=0), so it's aromatic The carbocation hasThe Huckel 4n2 pi electrons rule cyclic shaped ring molecule follows huckel rule if the total number of pi electrons belong to the molecules can be equated to the " 4n2" formula , where n can be any natural number molecules can be equated to the " 4n2" formula , where n can be any natural number



Solved 1 According To Huckel S Rule How Many Pi A 4n 2 Chegg Com



13 6 Aromaticity Organic Chemistry Ii
But, antiaromatic compounds have a closed loop of 4n pibond electrons Below are the piorbital diagrams of benzene, the most identifiable aromatic compound Each of the three double bonds contributes 2 pielectrons over 6 atoms, for a total of 4*12=6 electrons, in a ring, in a piorbital that is planar Therefore it is aromaticIn keeping with the MöbiusHückel concept, a cyclic ring molecule follows Hückel's rule when the number of its πelectrons equals 4n 2 where n is a nonnegative integer, although clearcut examples are really only established for values of n = 0 up to about n = 6Thermal rearrangements of all conjugated systems containing 4n 2 pi electron are stereospecificThis is based on preservation of orbital symmetry in the highest occupied molecular orbitalSystems containing 4n pi electrons show the opposite conrotatory mode This is also true for rearrangements of 4n 2 pi (where n is a whole number) electrons driven by light (photoinduced)



Why Is Cyclopropene Non Aromatic Quora



Is Tropone Aromatic Chemistry Stack Exchange
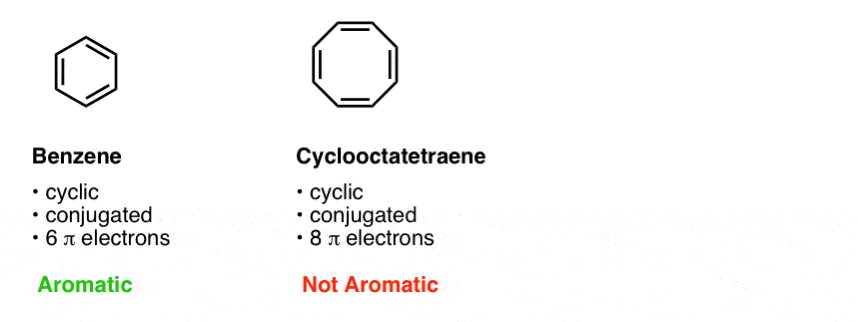
The ring obeys the Hückel's rule, which states that the number of electrons in the loop of latex \pi /latex electrons is equal to 4n 2, where n is zero or a positive whole number As is evident from the above examples, determining whether a ring obeys the Hückel's rule or not using the Lewis diagram is straightforwardThe pi electron count is defined by the series of numbers generated from 4n2 where n = zero or any positive integer (ie, n = 0, 1, 2, etc) The most common case in six pi electrons (n = 1) which is found for example in benzene, pyrrole, furan, and pyridineCondition 3 The Molecule Must Have 4n2 Pi Electrons {The Huckel Rule} The third condition is that the cyclic, conjugated molecule must have 4n2 pi electrons Benzene and cyclooctatetraene are both cyclic and conjugated, but benzene is aromatic and cyclooctatetraene is not
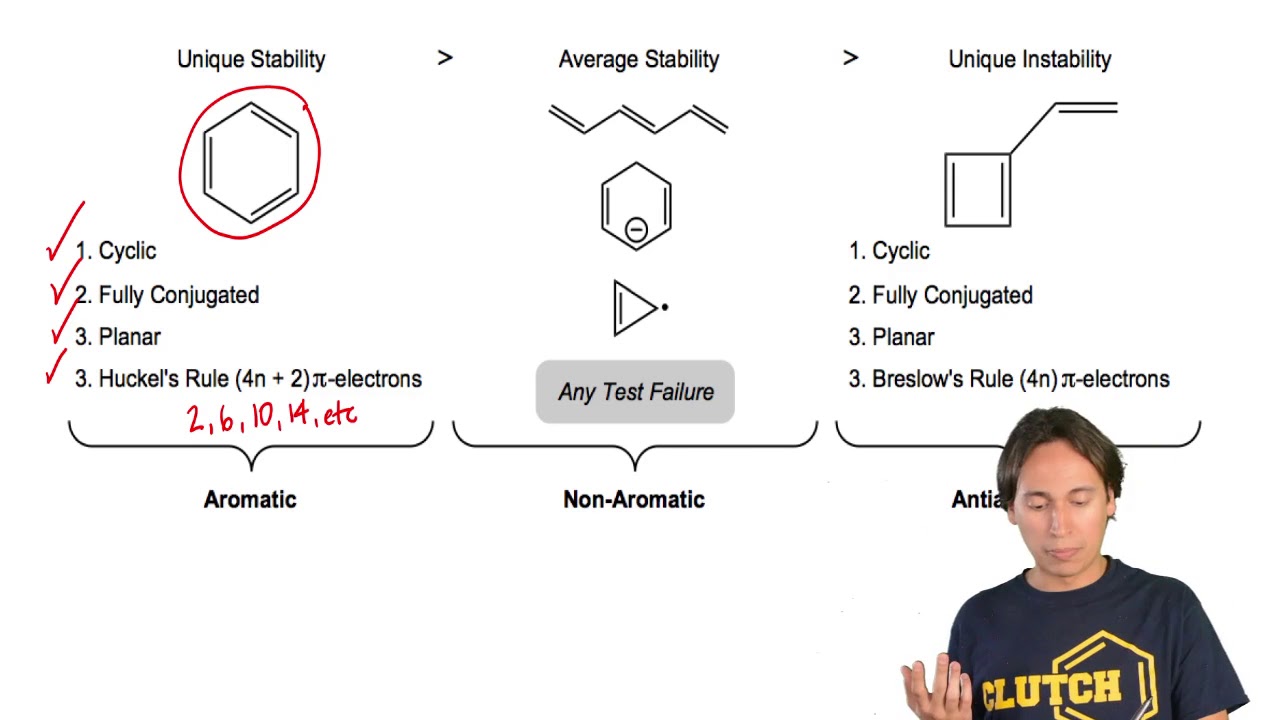


Huckel S Rule Organic Chemistry Video Clutch Prep



Phenanthrene Is Antiaromatic Chemistry Questions
Lithium Li AN = 3, # electrons =3 1s22s1 Li AN = 3, # electrons = 2 1s2 • unstable openshell atoms could be made stable by adding (to form anions) or subtracting (to form cations) electrons to provide ions with complete outer shells • aromatic anions and cations can also be formed if the 4n2 Huckel number of pi electrons resultsThe following compound is not aromatic even though it has 4 n2 \\pi electrons in a continuous cyclic array Explain why this compound is not aromatic (Hint DHe told me that if the delocalized pi electrons of a cyclic compound can be denoted as 4n2 where "n" is an integer, then the compound can be called aromatic And in the case of cyclopropene, if the pi electrons were delocalized then there would be 2=4n2, giving n=0, an integer Hence the question, $\endgroup$ – Habib Oct 30 ' at 855



What Is The Difference Between Anti Aromatic And Non Aromatic Species Quora
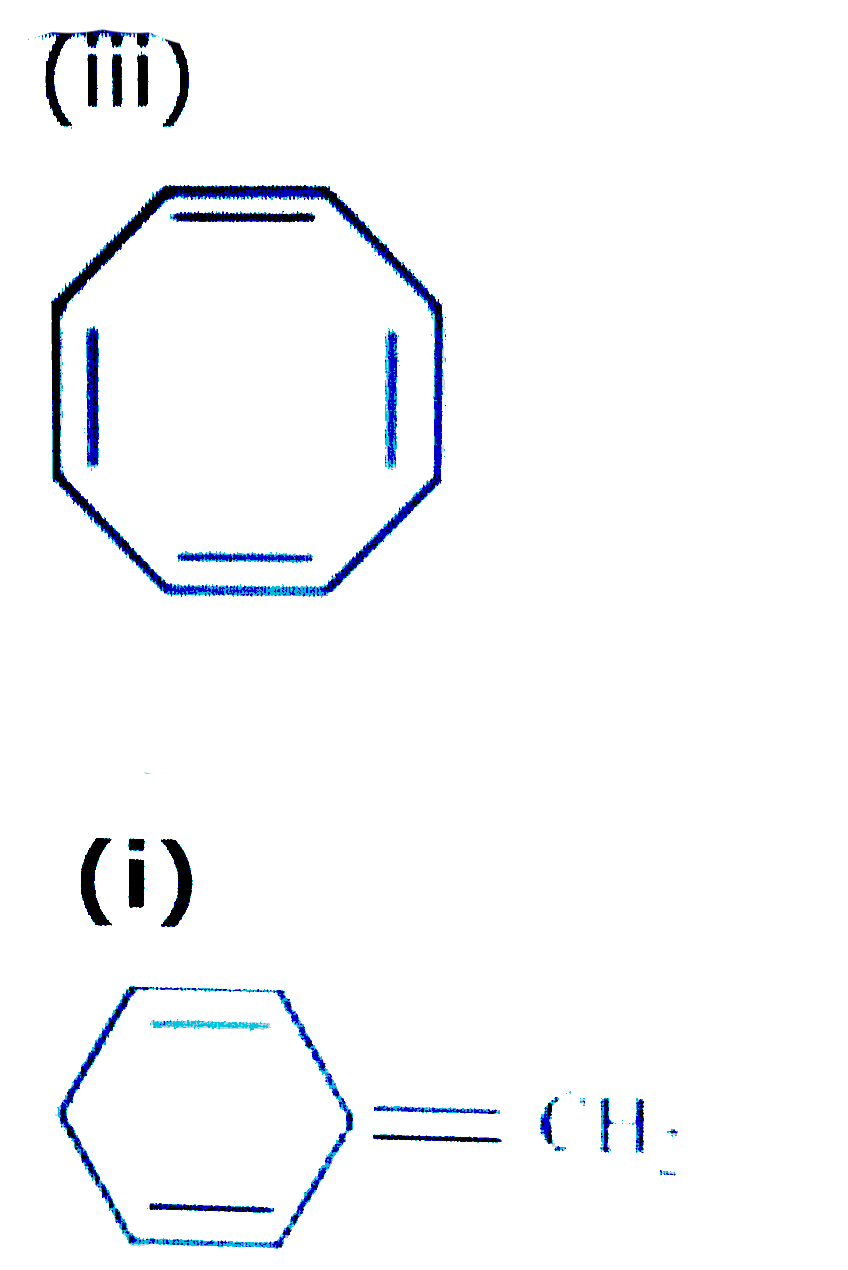


Explain Why The Following Systems Are Not Aromatic Img Src Http
The following compound is not aromatic even though it has 4 n2 \\pi electrons in a continuous cyclic array Explain why this compound is not aromatic (Hint DBenzene has 6 pielectrons and (4× 1)2 = 6, thus it obeys Huckel's Rule while cyclooctatetraene has 8 pielectrons 4n2 ≠ 8, thus it does not follow Huckel's Rule So, benzene is aromatic and cyclooctatetraene is a nonaromatic compoundAn aromatic compound must have 4n 2 pi electrons (where n is a whole number = 0, 1, 2, etc) Generally, aromatic compounds are nonpolar Therefore, they are immiscible with water The carbontohydrogen ratio is less in aromatic compounds Most aromatic compounds undergo electrophilic substitution reactions Due to the presence of


Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry



Oneclass 1 Classify The Following Compounds As Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Nonaromatic 8 Points P
The math(4n2)\pi/math rule is commonly called the Hückel's rule Theoretically,it is used to determine whether a compound is an aromatic compound or not For a compound to be an aromatic compound, it should obey the following 1 It should haThermal rearrangements of all conjugated systems containing 4n 2 pi electron are stereospecificThis is based on preservation of orbital symmetry in the highest occupied molecular orbitalSystems containing 4n pi electrons show the opposite conrotatory mode This is also true for rearrangements of 4n 2 pi (where n is a whole number) electrons driven by light (photoinduced)We not only consider pi electrons, we also consider lone pair or negative charge in 4n2 4n2 is the total number of electrons taking part in conjugation and not just pi electrons!
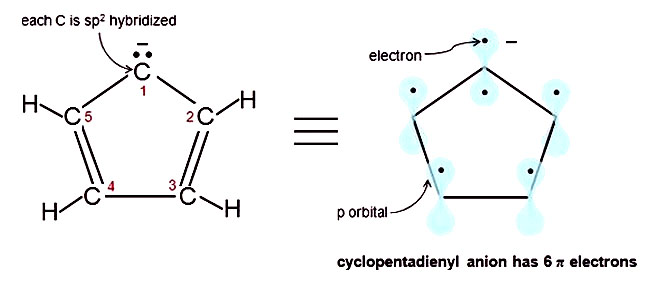


Learn Aromatic 4n 2 Electrons Meaning Concepts Formulas Through Study Material Notes Embibe Com
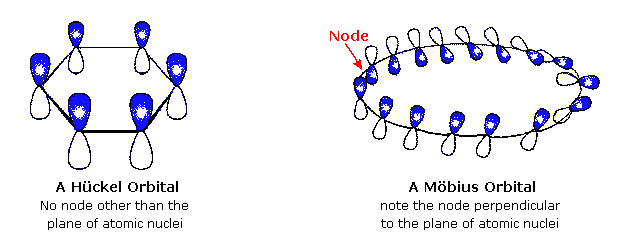


A Mobius 16 Pi Electron System
And I have filled the bonding molecular orbitals of benzene So I have represented all 6 pi electrons If I think about Huckel's rule, 4n plus 2, I have 6 pi electrons So if n is equal to 1, Huckel's rule is satisfied Because I would do 4 times 1, plus 2 And so I would get a total of 6 pi electrons And so 6 pi electrons follows Huckel's ruleAny compound with 4n 2 pi electrons will be aromatic True False The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS) increases if you place electronwithdrawing groups on the benzene ring True False FriedelCrafts Acylation is usually better than FriedelCrafts Alkylation for obtaining monosubstitution productsHuckel's Rule (4n2 rule) In order to be aromatic,a molecule must have a certain number of pi electrons within a closed loop of parallel, adjacent p orbitals The pi electron count is defined by the series 4n2 where n = zero or a positive integer (0, 1, 2, etc) The most common examples are Furan, Pyrolle, Naphthalene, Anthracene etc
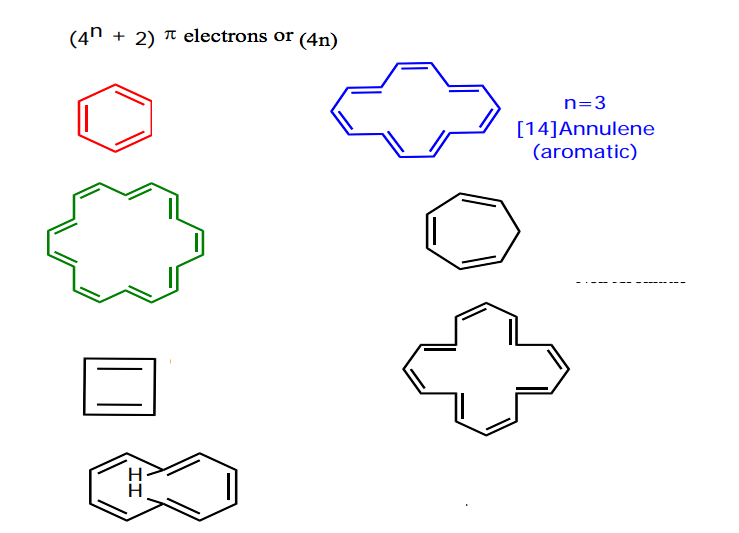


Solved 4 N 2 Pi Electrons Or 4 N Chegg Com
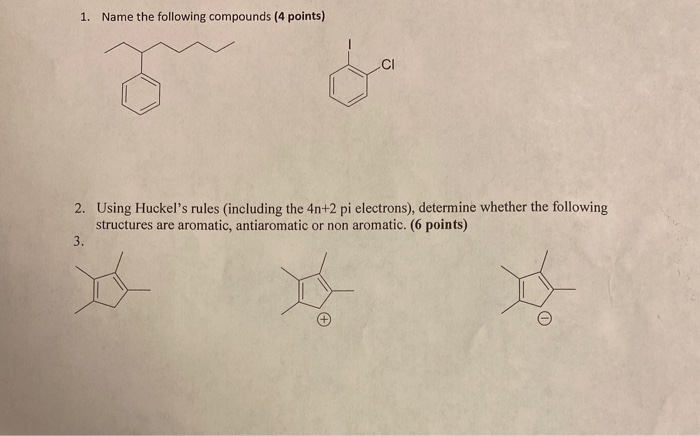


Solved 1 Name The Following Compounds 4 Points 2 Usin Chegg Com
The following compound is not aromatic even though it has 4 n2 \\pi electrons in a continuous cyclic array Explain why this compound is not aromatic (Hint DCondition 3 The Molecule Must Have 4n2 Pi Electrons {The Huckel Rule} The third condition is that the cyclic, conjugated molecule must have 4n2 pi electrons Benzene and cyclooctatetraene are both cyclic and conjugated, but benzene is aromatic and cyclooctatetraene is notOption C is correct There must be conjugation of the pi electron system Option D is correct, they must possess 4n 2 pi electrons This is referred to as the Huckel's rule Option B is wrong This is simply because we have compounds which are not monocyclic and are aromatic Example of this is anthracene and naphthalene



Applying The Criteria For Aromaticity Mcc Organic Chemistry



Directivity And Ring Activation Deactivation Ppt Video Online Download
If oxygen contributes any pi electrons, the molecule will have 12 pi electrons, or 4n pi electrons, and become antiarmoatic As it is now, the compound is antiaromatic Nitrogen cannot give any pi electrons because it's lone pair is in an sp 2 orbital Boron has no pi electrons to give, and only has an empty p orbitalWell, the requirements for aromaticity are Planar ring 4n 2 pi electrons Delocalization of electrons throughout the ring (ie conjugated pi system) Drawing out imidazole, we get LOCALIZED VS DELOCALIZED I would examine the electron geometries to check whether or not all the lone pairs of electrons supposedly conjugated throughout the system are in an orbital that is perpendicular to theSo while aromatic molecules have (4n2) pi electrons, the "rule" for anti aromatic molecules is (4n) (This unusual instability is called "antiaromaticity" This means that we can now draw up three categories for molecules according to the following criteria Aromatic molecules are cyclic, conjugated, have (4n2) pi electrons, and are



Indeno 1 2 B Fluorene Based 2 2 Cyclophanes With 4n 4n And 4n 4n 2 P Electrons Syntheses Structural Analyses And Excitonic Coupling Properties Wang 19 Angewandte Chemie Wiley Online Library


Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Non Aromatic 13 Worked Examples
In Huckel's `(4n2)pi` rule for aromaticity, 'n' represents In Huckel's `(4n2)pi` rule for aromaticity, 'n' represents Books Physics NCERT DC Pandey Sunil Batra HC Verma Pradeep Errorless Chemistry electrons=2,6,10,14 Related Video View All For any compound to be aromatic, compound should follow a cartain rule known as Huckel'sIf n=1, 4n2 = 6 > 6 pi electrons in a ring is aromatic > benzene is an example if the number of pi electrons does NOT equal 4n2 for any value of n, the ring is not aromatic > example here is butadiene furan 2 double bonds in the ring, and 1 lone pair on the O participate in pi bonding total of 6 pi electrons, ring is aromaticHuckel's Rule (4n2 rule) In order to be aromatic,a molecule must have a certain number of pi electrons within a closed loop of parallel, adjacent p orbitals The pi electron count is defined by the series 4n2 where n = zero or a positive integer (0, 1, 2, etc) The most common examples are Furan, Pyrolle, Naphthalene, Anthracene etc


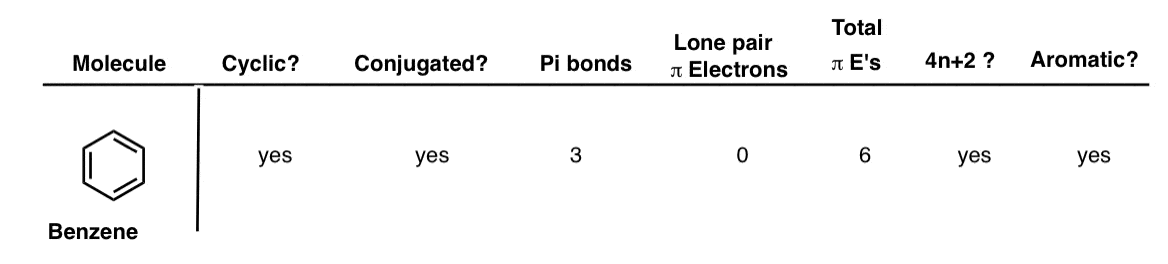
Double Aromaticity Arising From S And P Rings Communications Chemistry



Which Of The Following Species Is Not Aromatic
The huckel rule just says (it was discovered empirically, later confirmed by calculations ) that all systems with 4n2 pielectrons (6, 10, etc) are extremely stable and do nor behave like normal2) it has a cyclis ring structure,(2nd condition fulfilled) 3) A benzene molecule contains 3 single & 3 double bond Hence the total no of pi electrons= 3*03*2=6 putting n=1, hence 4n2=6 Hence benzene follows 4n2 rule(3rd condition fulfilled) all the conditions being fulfilled Benzene may be looked upon as an aromatic compoundThat what Huckel's Rule gives, those number of pielectrons in aromatic molecules Given the structures of aromatic molecules, the number of pielectrons has to be 2, 6, 10, 14, 18, 22, etc That series of numbers pertains to a mathematical sequence 4n2 So, the "n" only pertains to whichever number of pielectrons you are looking at



Aromatic Stability Iii Video Khan Academy


Aromaticity Rules And Definition Organic Chemistry Help



15 4 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libretexts



Huckel S Rule Organic Chemistry Video Clutch Prep
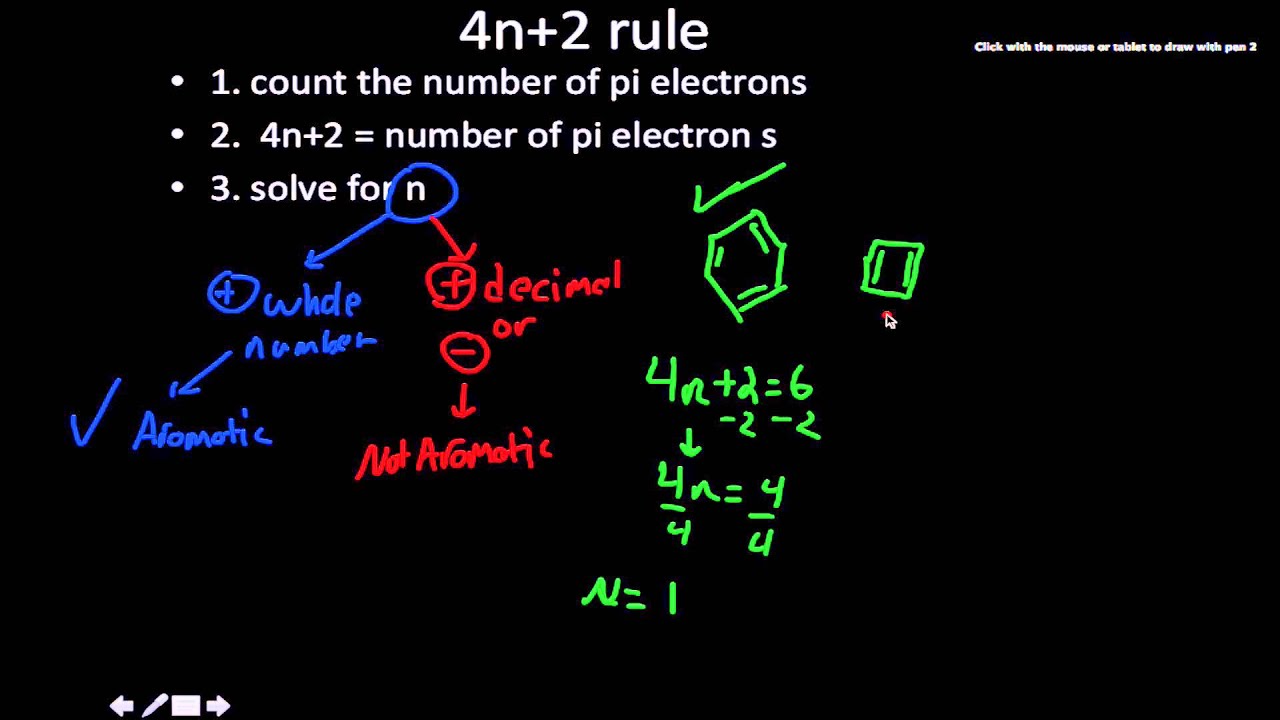


4n 2 Rule Youtube



Aromatic Molecules Contain P Electro Clutch Prep
.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=369&height=173)


15 3 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libretexts



Mobius Aromaticity Wikipedia



Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Nonaromatic Compounds Chemistry Steps
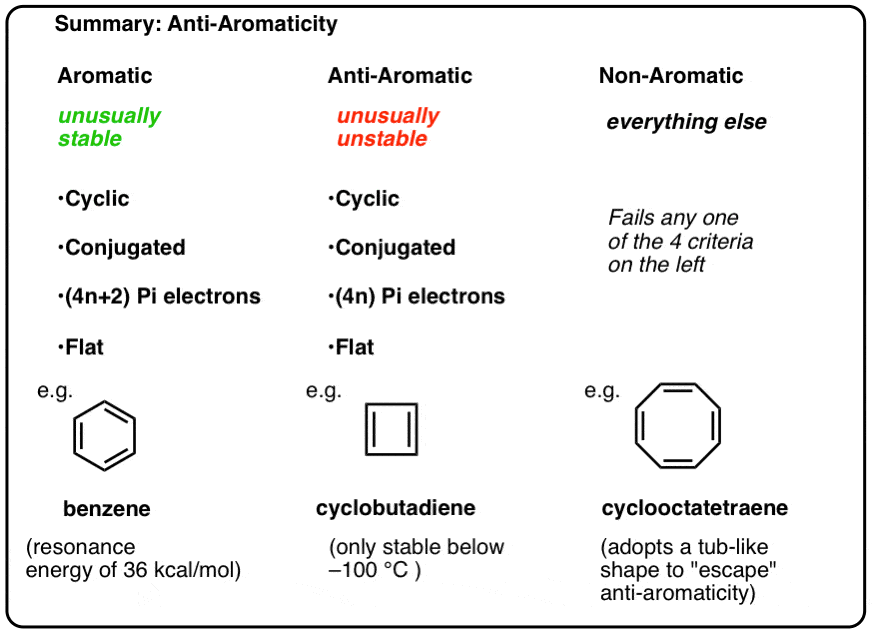


Antiaromaticity And Antiaromatic Compounds Master Organic Chemistry
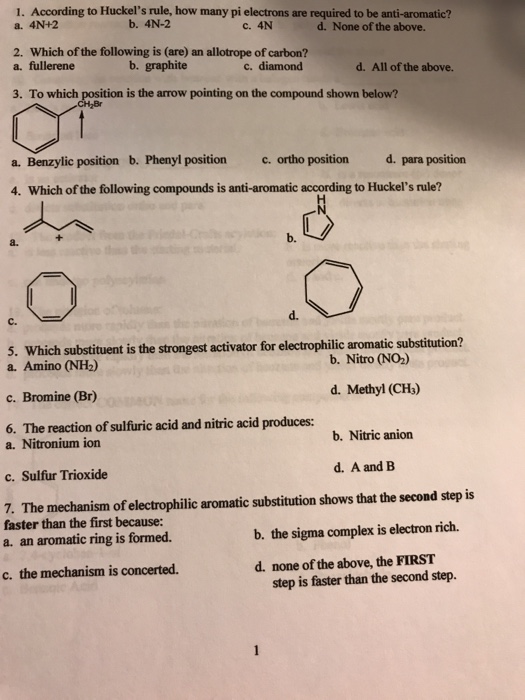


Solved 1 According To Huckel S Rule How Many Pi Electro Chegg Com
.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=440&height=181)


15 4 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libretexts
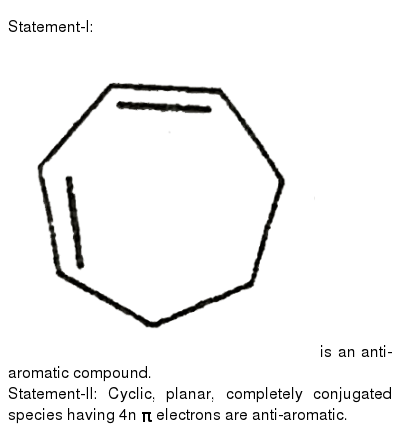


According To Huckel Rule An Aromatic Compound Must Possess



Which Of The Following Structures Qualify As Being Aromatic According To Huckel S Rule Homeworklib
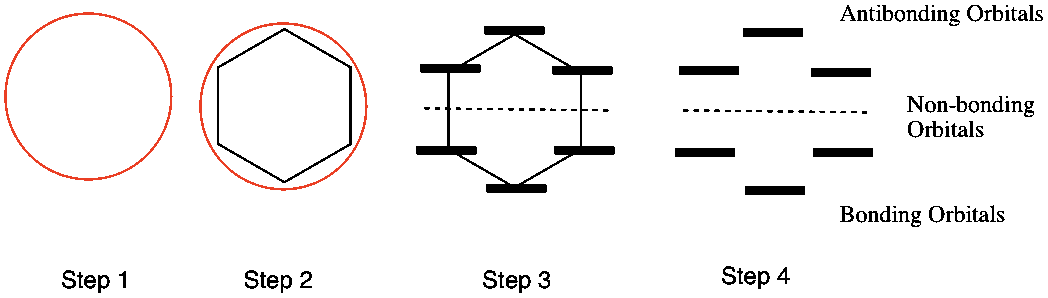


Huckel Aromaticity And Frost Circles Organic Chemistry Help



Aromatic Compounds Benzene Its Family Nanoplasmonic Research Group Organic Chemistry Chapter 4 Part I Ppt Download
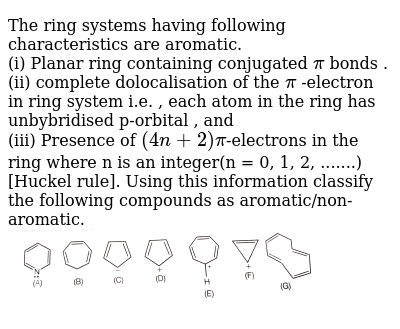


In Huckel S Rule 4n 2 P Electrons What Does N Signifies



Huckel S Rule Explanation Of Huckel S 4n 2 Rule To Estimate Aromaticity



Solved Why Is The Following Compound Not Aromatic Oit Is Chegg Com



Classics Illustrated Clar S Sextet And Huckel S 4n 2 P Electron Rules The Journal Of Physical Chemistry C X Mol



31 04 Criteria For Aromaticity Youtube
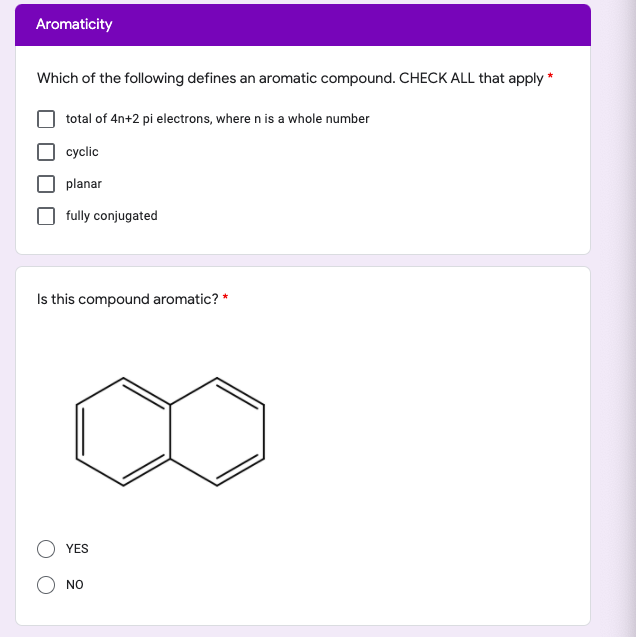


Solved Aromaticity Which Of The Following Defines An Arom Chegg Com
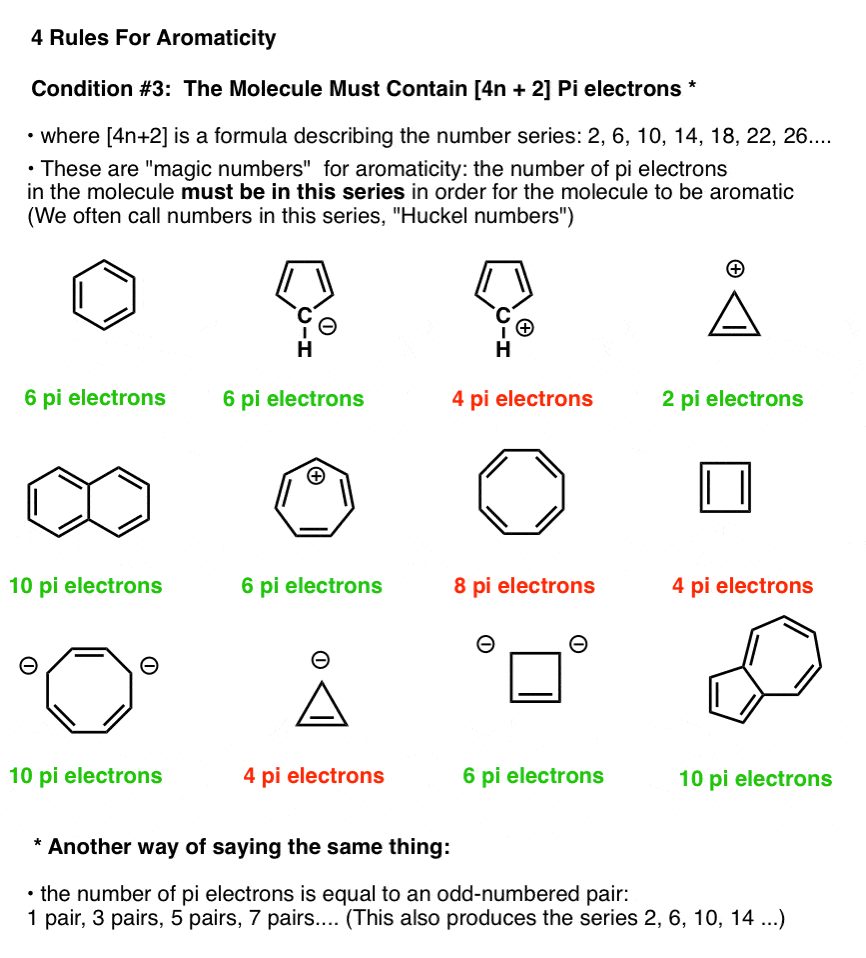


Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry



130 Aromaticity 23 What Is So Special About 4n 2 P Electrons Madoverchemistry Com
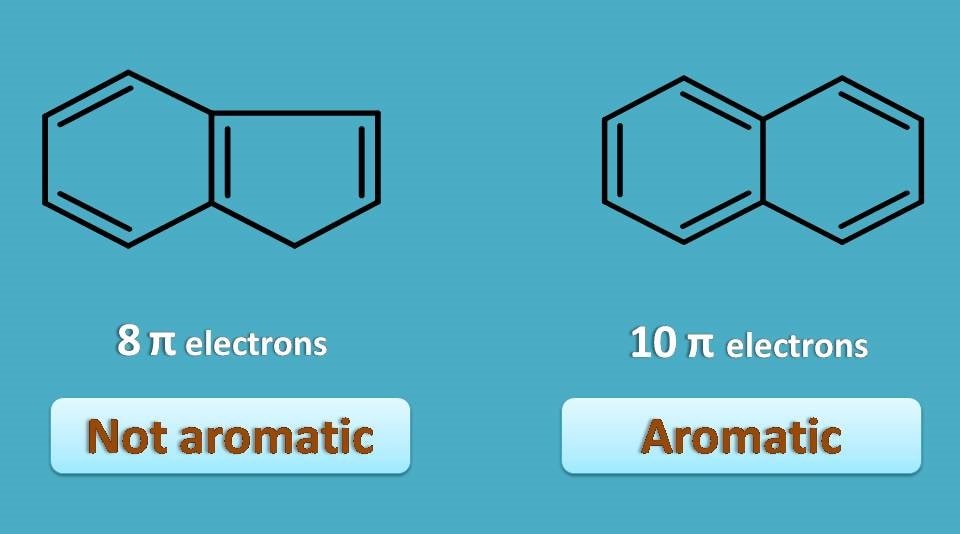


Aromaticity 4 Criteria Every Compound Needs



Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Non Aromatic 13 Worked Examples


Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Term



Why Is Cyclooctatetraene A Non Aromatic Compound Quora



Excited State Proton Transfer Relieves Antiaromaticity In Molecules Pnas
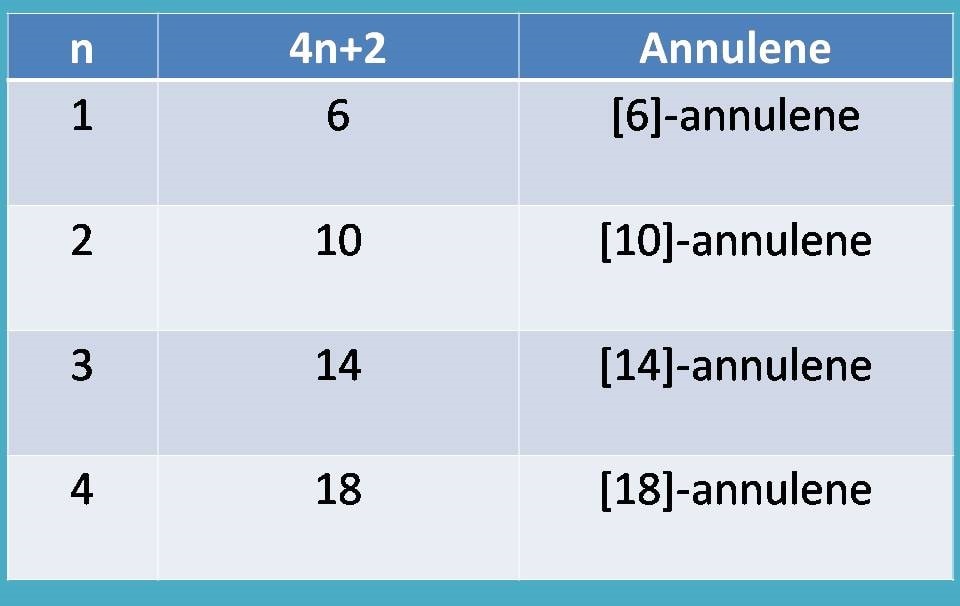


Aromatic Compounds Who Really We Are
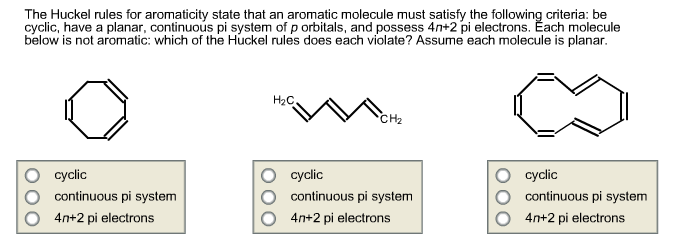


Solved The Huckel Rules For Aromaticity State That An Aro Chegg Com


Aromaticity Rules And Definition Organic Chemistry Help



The Criteria For Aromaticity Mcc Organic Chemistry


A Disrotatory 4n 2 Electron Anti Aromatic Mobius Transition State For A Thermal Electrocyclic Reaction Henry Rzepa S Blog
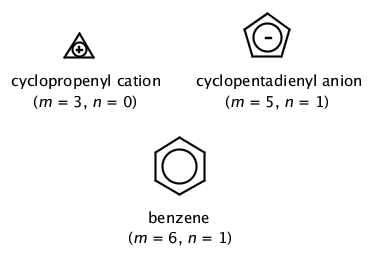


Iupac Huckel 4 Em N Em 2 Rule H


Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Term
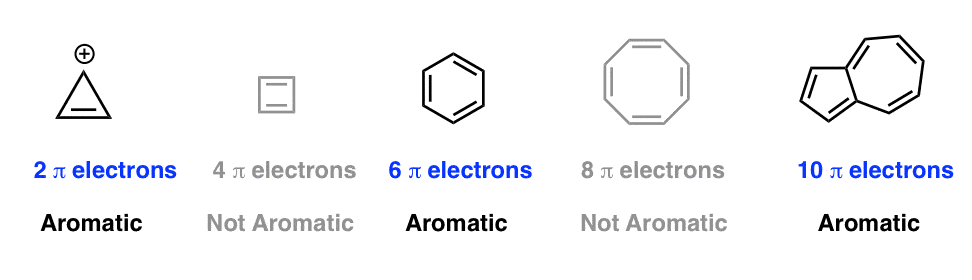


Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry


Aromatic Ouroboroi Heterocycles Involving A S Donor Acceptor Bond And 4n 2 P Electrons Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics Rsc Publishing
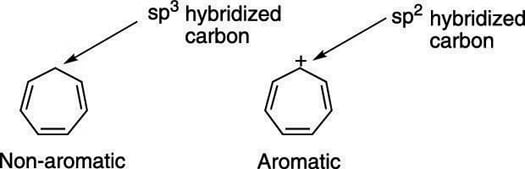


How To Determine The Aromaticity Of A Ring System Dummies


Multiple Choice Answers 353 Fin W17
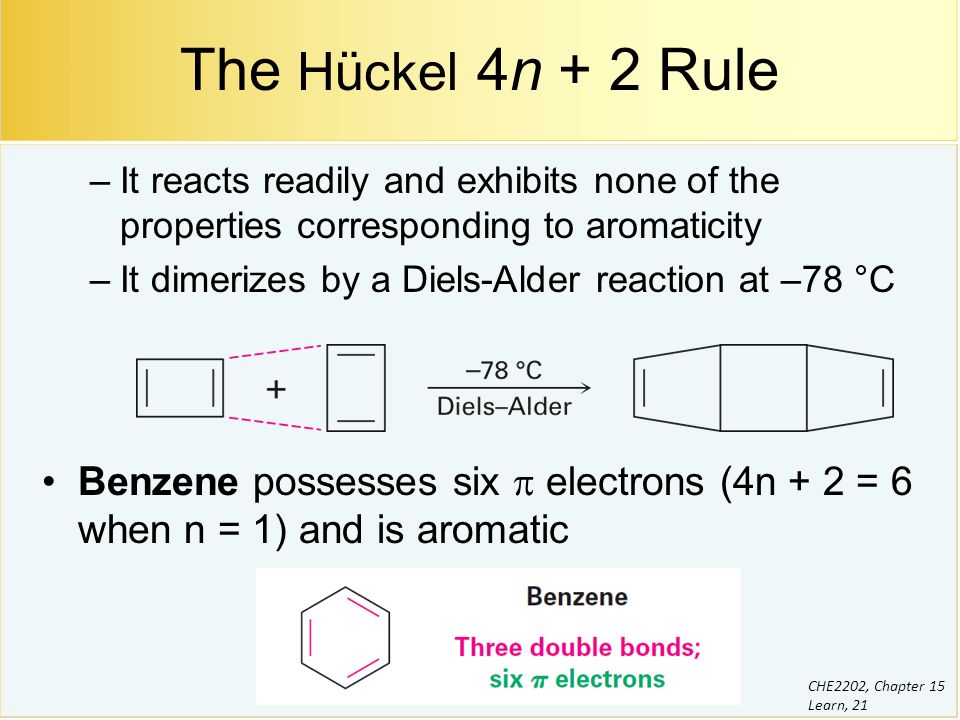


Benzene And Aromaticity Ppt Video Online Download
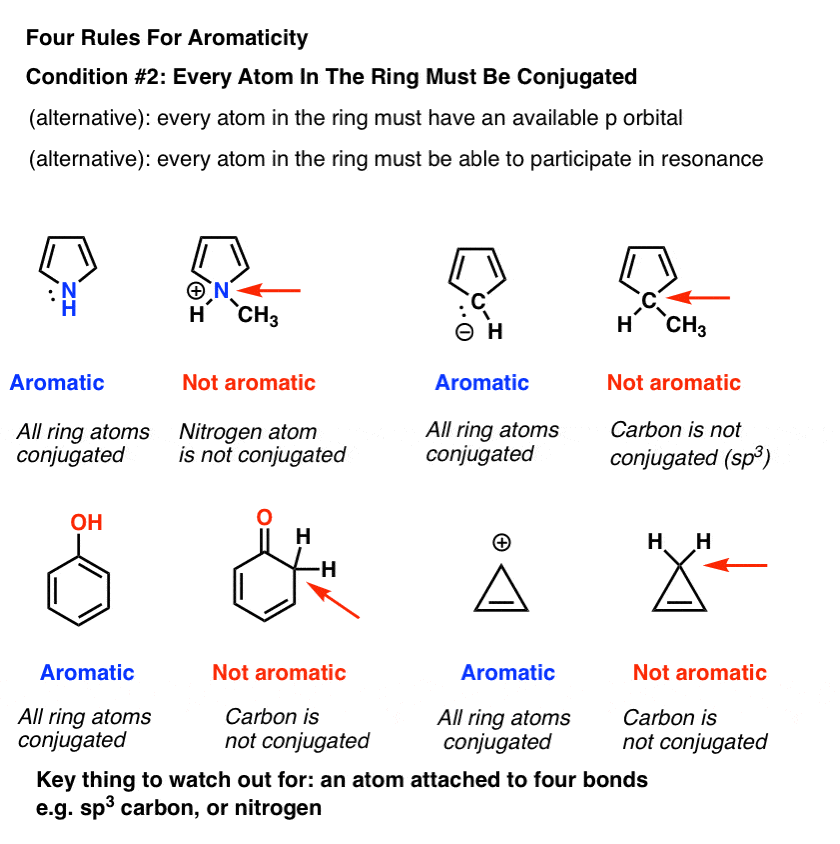


Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry



Indicate Whether Each Structure Is Aromati Clutch Prep



Huckel S Rule Definition Formula And Examples
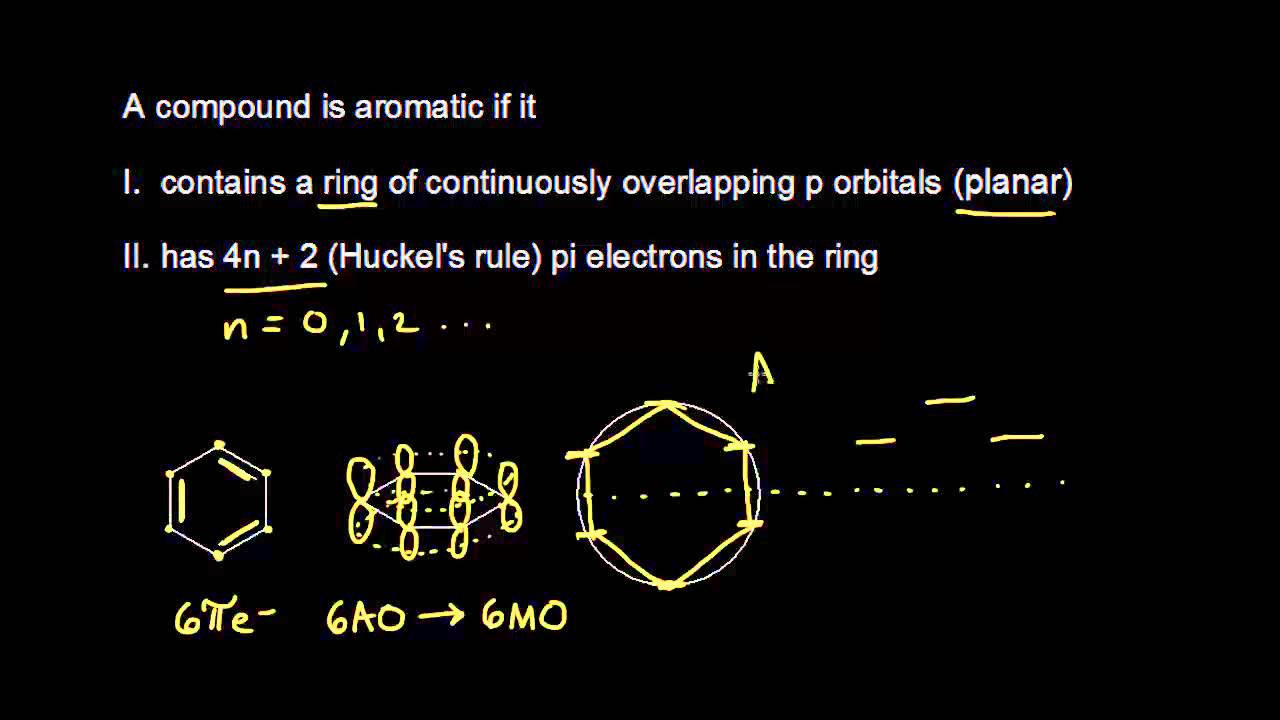


Aromatic Stability I Video Khan Academy
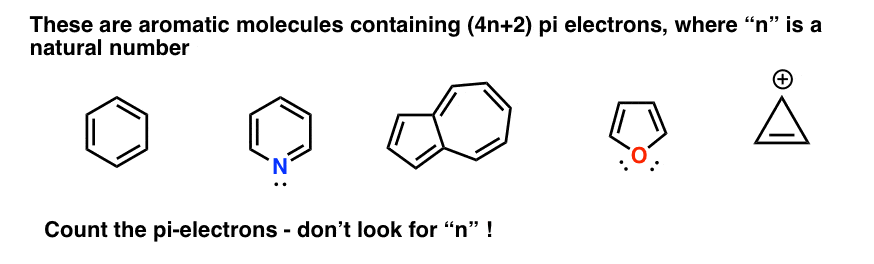


Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry
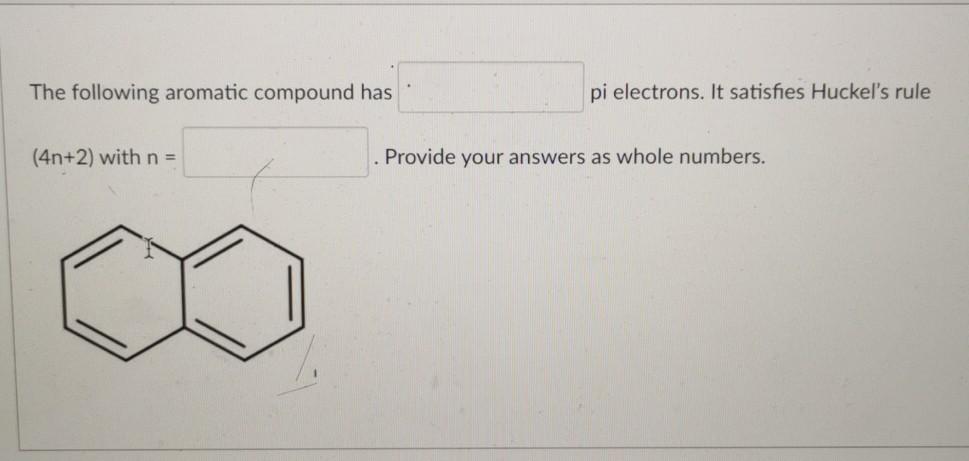


Solved The Following Aromatic Compound Has Pi Electrons Chegg Com



109 Aromaticity 2 Huckel S Rule Madoverchemistry Com



Identifying Aromatic Compounds Organic Chemistry
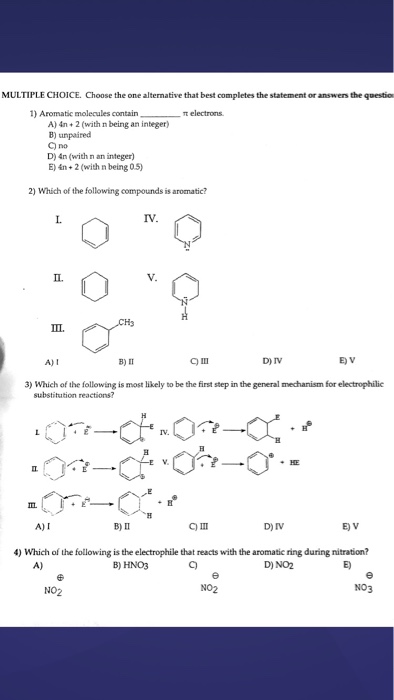


Solved Aromatic Molecules Contain Pi Electrons A 4n Chegg Com



Aromatic Compounds 15 7 Introduction To Aromatic Compounds Ppt Download
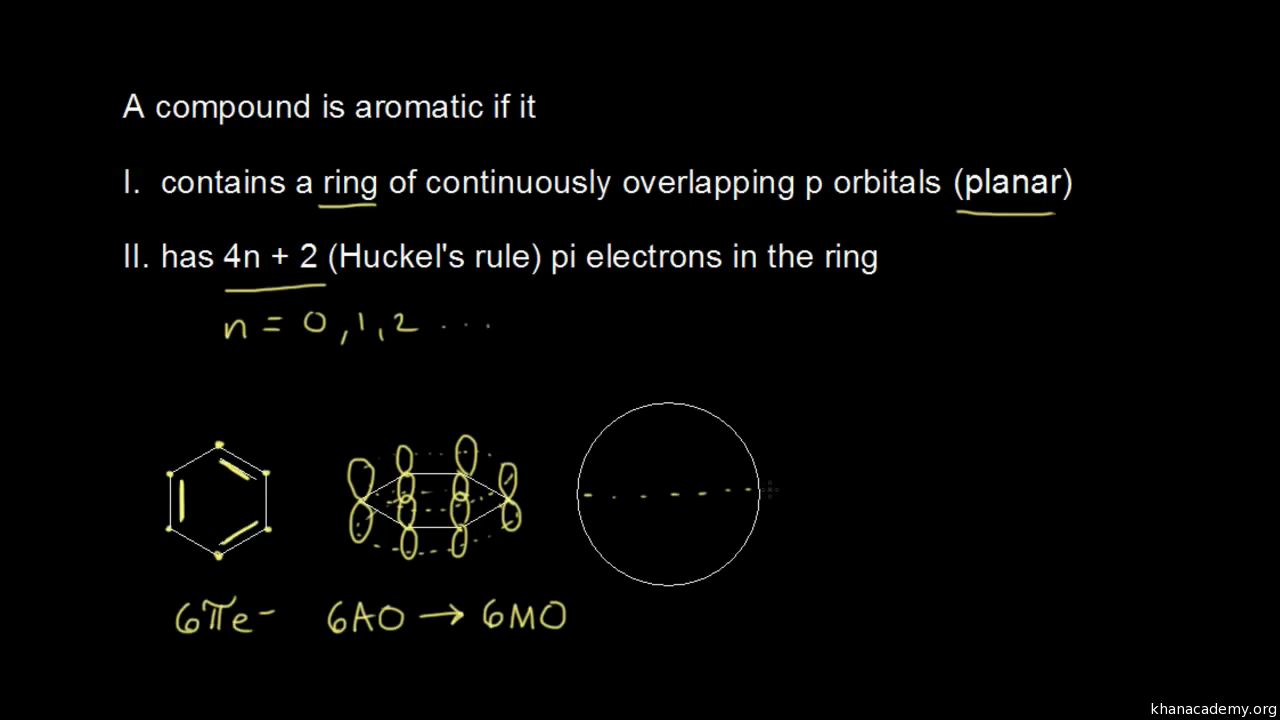


Aromatic Stability I Video Khan Academy
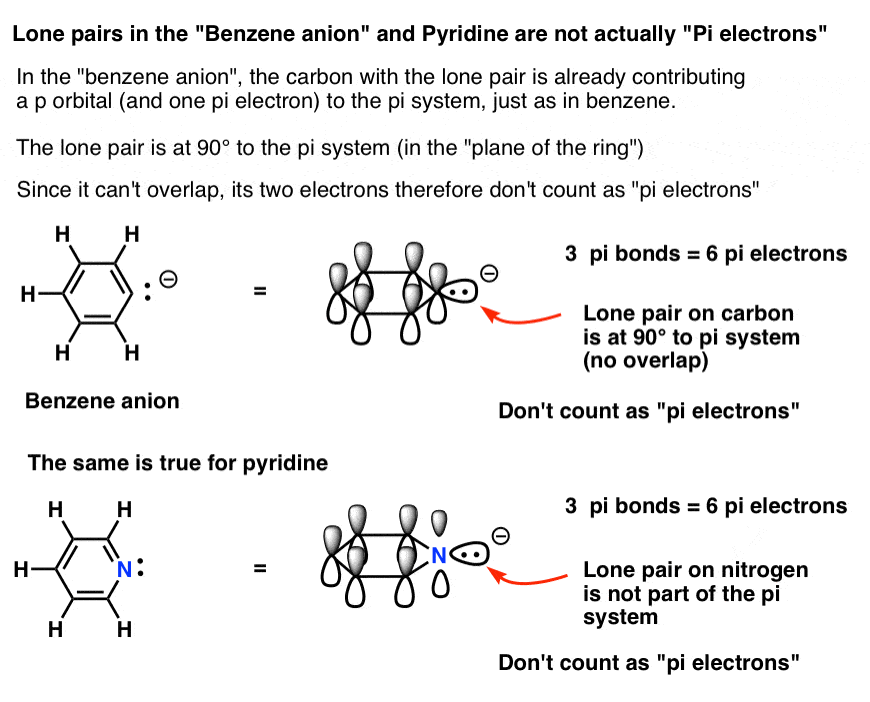


Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry
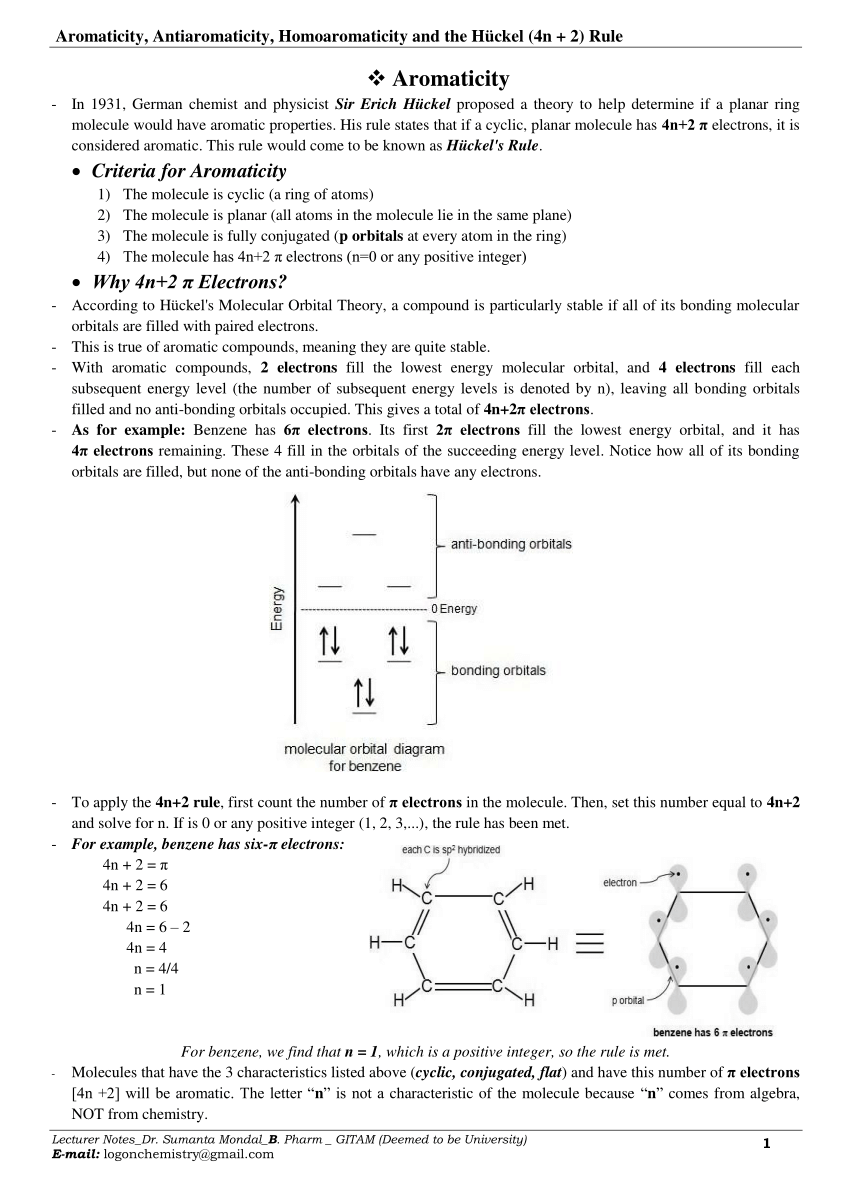


Pdf Aromaticity Antiaromaticity Homoaromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule



In Huckel S 4n 2 Pi Rule For Aromaticity N Represents



What Is An Aromatic Compound Definition Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
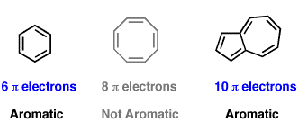


Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry



Why Is Porphyrin Aromatic Chemistry Stack Exchange



Aromatic Stability Ii Video Khan Academy



Aromaticity Rules Ketogenic Diet Ketogenic Diet



Huckel S Rule Aromatic And Antiaromatic Compounds Chemistry Steps



Aromaticity



Huckel S Rule Aromatic And Antiaromatic Compounds Chemistry Steps


Properties Of Aromatic Compounds Chemistry Revision Site



What Is An Aromatic Compound Definition Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



How Is Anthracene Aromatic Quora
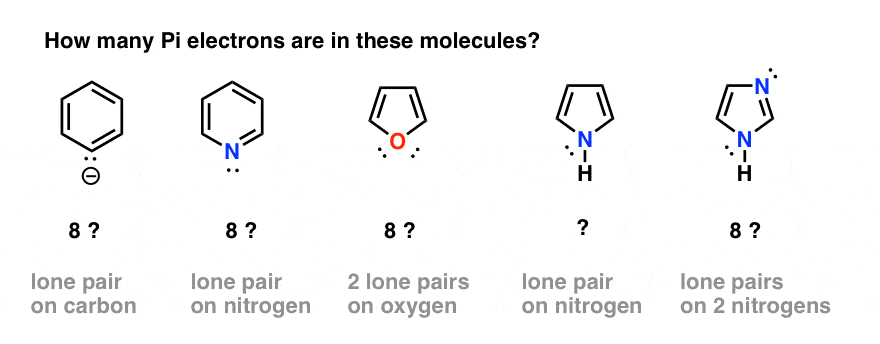


Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry
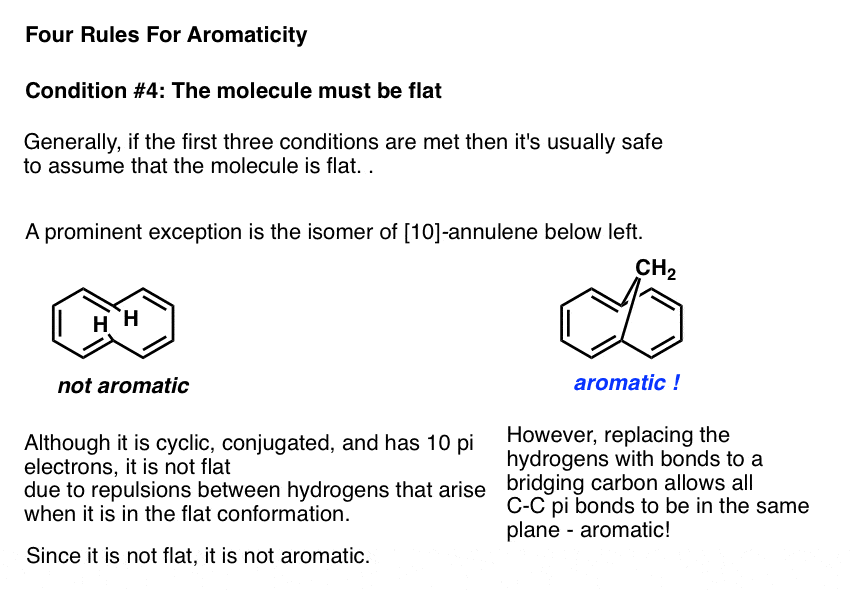


Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry



The Concept Of Aromaticity Chempapy



Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Nonaromatic Compounds Chemistry Steps



Huckel S Rule Definition Formula And Examples
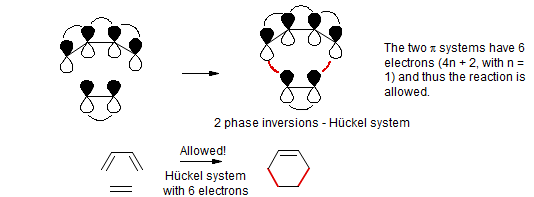


Pericyclic Reactions The Dewar Zimmerman Moebius Huckel Approach



109 Aromaticity 2 Huckel S Rule Madoverchemistry Com



Oneclass A Label Each Compound Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Nonaromatic B Give The Number Of Pi Ele



130 Aromaticity 23 What Is So Special About 4n 2 P Electrons Madoverchemistry Com



Huckel S Rule Aromatic And Antiaromatic Compounds Chemistry Steps
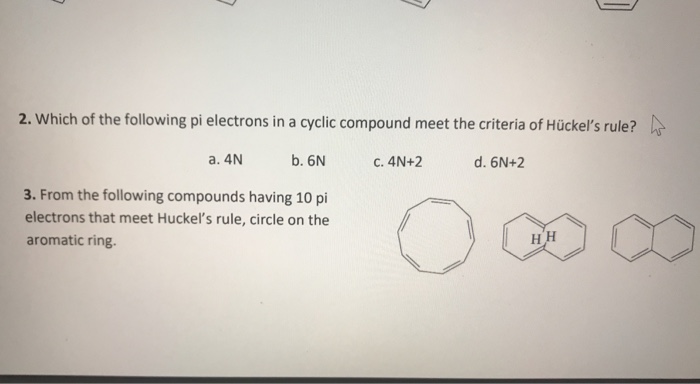


Solved 2 Which Of The Following Pi Electrons In A Cyclic Chegg Com



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿